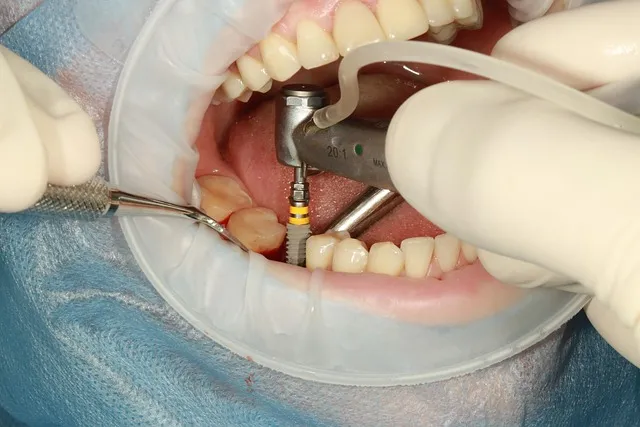
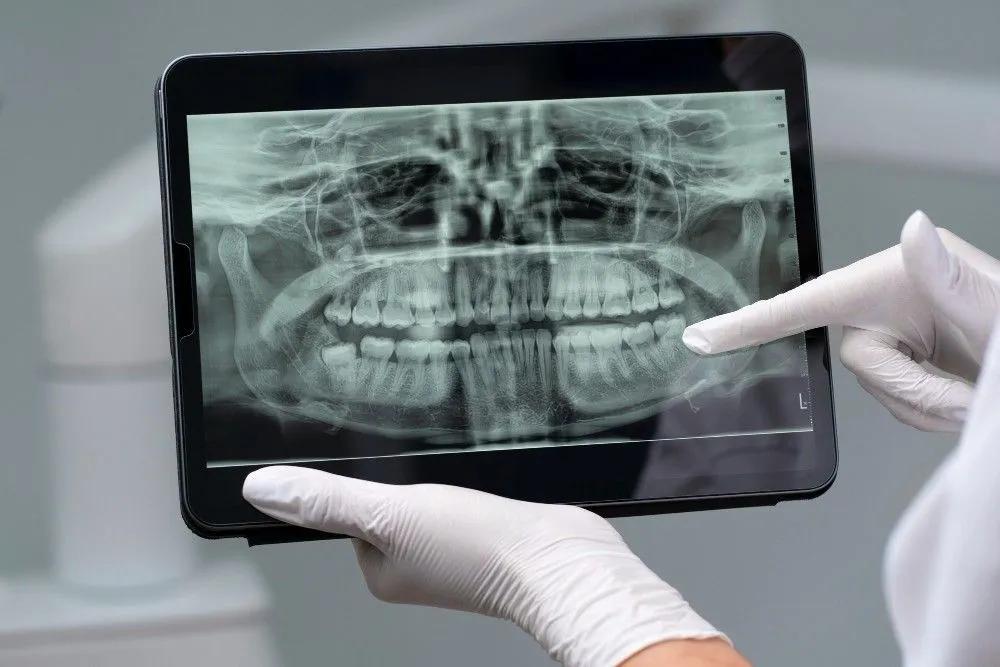
Mouth pain, swollen gums, and red gums? Eating and drinking issues? are diagnosed with Bacterial infection mouth? You must receive the proper treatment for your oral infection, which bacterial or fungal illnesses may bring on.
Please continue reading to find out what causes Mouth Bacterial infections, how to treat them, and how to deal with the pain they bring.

 Symptoms could consist of, but not be limited to:
Symptoms could consist of, but not be limited to:

What is a Mouth Bacterial Infection?
Mouth infections are inflammations of the teeth, gums, or facial bones in the oral cavity. These inflammations are most frequently brought on by: Bacteria. Bacterial overgrowth can result in tooth abscesses and oral infections. Any infection can develop into sepsis if left untreated. Thus it's critical to treat tooth infections as soon as possible. Thrush infections in the mouth can be brought on by the fungus Candida. It exhibits symptoms different from those of a bacterial infection and necessitates a different treatment.Good bacteria, how does it work?
While it could initially seem a little terrifying, bacteria in the mouth is generally a healthy thing. The "good bacteria" maintains the oral balance, which acts in the interests of human health. However, other kinds of bacteria aren't good for your mouth or teeth; these unfavorable bacteria can eventually cause infections in the mouth and other problems, including periodontitis. As a result of this severe gum infection, your gums are starting to pull away from your teeth.Potential Causes of Bacterial mouth infection -
Some common causes of Bacterial infection mouth may include:
- Dental plaque: This is a thin film of bacteria that forms on the teeth and gums. It can lead to gum disease if not removed through regular brushing and flossing.
- Poor oral hygiene: If you don't brush and floss regularly, bacteria can build up in your mouth, leading to infections.
- Dentures: If you wear dentures and don't clean them properly, bacteria can build up and cause infections.
- Illnesses: Some illnesses, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, can weaken the immune system and make you more susceptible to bacterial infections in the mouth.
Types of mouth bacterial infections -
A few common bacterial infections are:
Dental caries:
it is the medical word for tooth decay, sometimes known as cavities. This occurs when acid produced by bacteria from leftover sugars and carbohydrates in the mouth eats away at a tooth's enamel and the dentin that lies beneath it. Early detection of decay allows it to be reversed, but if it is not treated soon, it can eat through the tooth's root.Gingivitis:
Plaque accumulation on the teeth can lead to gum tissue irritation and gum disease, known as gingivitis. The naturally occurring film of bacteria known as plaque adheres to teeth and releases toxins that irritate the gums. Your gums may swell, bleed, and turn red; if untreated, periodontitis may develop.Periodontitis:
A dangerous gum condition called periodontitis affects soft tissue and kills the bone that supports your teeth. If left untreated, plaque buildup slowly deteriorates the teeth and may result in tooth loss. Periodontitis can be classified as chronic, aggressive, or necrotizing. Periodontitis can enter your bloodstream and impact other areas of your body if neglected.A pus-filled pocket
A pus filled pocket called an abscessed tooth can develop in various dental structures due to a bacterial infection. Bacteria infiltrate the teeth and gums through cavities or gum disease already present to produce this. It may also be brought on by a foreign body, such as a popcorn kernel, lodged in your gums. If the infection is not treated, pain may spread to your jawbone, Neck, or ear. It has been documented to cause sepsis in the very rarest of circumstances.Symptoms of oral Bacterial infection -
Even though there are many distinct types of infections, they all have the same symptoms despite varied treatments. To prevent issues or an increased risk of significant health disorders, it's crucial to contact your dentist as soon as you notice any of these symptoms. Symptoms could consist of, but not be limited to:
Symptoms could consist of, but not be limited to:
- severe, excruciating dental pain
- Sensitivity to hot or cold conditions Neck, jawbone, or inner ear pain
- Fever
- unpleasant breath
- unpleasant aftertaste
- swelling in the cheek or face
- When chewing or biting, sensitivity
- gums that are swollen or red
- bleeding gums when you brush or floss
Treatments for bacterial infections -
Treatment for a bacterial infection in the mouth will depend on the specific type of infection and the severity of the symptoms. Common treatments include:
Antibiotics:
These medications can help kill the bacteria causing the infection.Pain medication:
Over-the-counter pain relievers can help manage pain and swelling.Mouth rinses:
Your doctor or dentist may recommend using a mouth rinse to help kill bacteria and reduce inflammation.Improved oral hygiene:
Brushing and flossing regularly and visiting the dentist regularly can help prevent bacterial infections in the mouth.Be sure to change your toothbrush regularly:
Dentists recommend a new toothbrush every 3-4 months.Use tongue scraper:
You must include a tongue scraper in your brushing routine to help eliminate bacteria that can accumulate on the tongue. If you think you may have a bacterial infection in the mouth, it's important to see a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.Final takeaway -
It's simple to maintain your mouth healthy and avoid oral infections. By often washing your hands, you lower the possibility of introducing foreign bacteria that might worsen pre-existing illnesses or cause infections in your mouth. It is imperative to stress the significance of twice-daily brushing and flossing. Cleaning your teeth properly is essential to remove plaque and maintain a healthy mouth. Avoiding tobacco use, eating healthful snacks, maintaining a balanced diet, and scheduling biannual cleanings and examinations with your dentist are all other strategies to prevent mouth infections.
Reviewed by