Gingivitis is a medium gum recession that produces inflammation and redness of the gingiva, or gum tissue near the base of the teeth. Knowing how to recognize the early indications of Gingivitis is critical so that you can act swiftly to help prevent the condition before it worsens.The good thing is that this frequent illness is easily treatable. A good personal dental care program of routine flossing and brushing, combined with regular dental appointments, can help eliminate Gingivitis while maintaining your gums healthy.Regularly inspect your mouth for initial indications of Gingivitis so that you can treat problems with a toothpaste-like periodontal. This article teaches about gingivitis early stage symptoms and their treatment.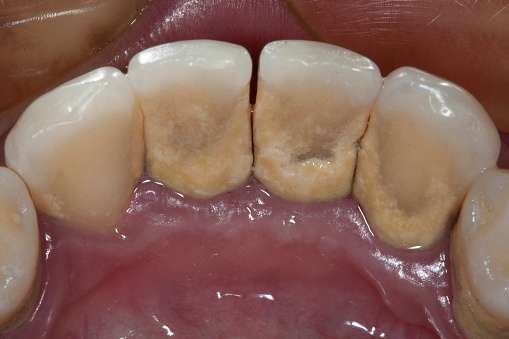 Gingivitis caused by dental plaque develops when plaque buildup affects a person's gums, causing inflammation, discoloration, and pain.
Gingivitis caused by dental plaque develops when plaque buildup affects a person's gums, causing inflammation, discoloration, and pain. Non Plaque-induced gingival lesions, on the other hand, can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi infection. Allergic reactions, infections, and reactions to foreign substances, such as prophylaxis foam particles, can also cause this kind of Gingivitis.If each kind of Gingivitis is not appropriately treated, they might proceed to periodontitis. Periodontitis is a greater ailment that can lead to subsequent issues such as tooth loss.Also Read: What Is the Difference Between a Bacterial and Viral Infection?
Non Plaque-induced gingival lesions, on the other hand, can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi infection. Allergic reactions, infections, and reactions to foreign substances, such as prophylaxis foam particles, can also cause this kind of Gingivitis.If each kind of Gingivitis is not appropriately treated, they might proceed to periodontitis. Periodontitis is a greater ailment that can lead to subsequent issues such as tooth loss.Also Read: What Is the Difference Between a Bacterial and Viral Infection?
What are the types of Gingivitis?
Gingivitis can be classified into two categories.Plaque -
 Gingivitis caused by dental plaque develops when plaque buildup affects a person's gums, causing inflammation, discoloration, and pain.
Gingivitis caused by dental plaque develops when plaque buildup affects a person's gums, causing inflammation, discoloration, and pain.Non-plaque -
 Non Plaque-induced gingival lesions, on the other hand, can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi infection. Allergic reactions, infections, and reactions to foreign substances, such as prophylaxis foam particles, can also cause this kind of Gingivitis.If each kind of Gingivitis is not appropriately treated, they might proceed to periodontitis. Periodontitis is a greater ailment that can lead to subsequent issues such as tooth loss.Also Read: What Is the Difference Between a Bacterial and Viral Infection?
Non Plaque-induced gingival lesions, on the other hand, can be caused by viruses, bacteria, or fungi infection. Allergic reactions, infections, and reactions to foreign substances, such as prophylaxis foam particles, can also cause this kind of Gingivitis.If each kind of Gingivitis is not appropriately treated, they might proceed to periodontitis. Periodontitis is a greater ailment that can lead to subsequent issues such as tooth loss.Also Read: What Is the Difference Between a Bacterial and Viral Infection?What are the symptoms of Gingivitis in the early stage?
While Gingivitis early stage symptoms can be unnoticed as they typically don't trigger pain, there are a few traditional markers to look for while flossing and brushing your teeth.1. Bad Breath -
Bad breath, commonly known as halitosis, is often discouraging, but may also indicate that you're acquiring gum disease.There are numerous causes of foul breath, but the most common are gases emitted by germs that cover your gums, teeth, and tongue. Food particles can also become stuck in the teeth & begin to rot, leading to an unpleasant odor. Brushing and flossing to remove odor-causing germs should help address the problem.2. Gum Bleeding -
Bleeding gums are one of the common symptoms of Gingivitis. Because healthy gums do not bleed, finding blood when flossing or brushing your teeth may indicate gum disease. Bleeding and swelling are caused by plaque buildup at the junction of the gums and indicate that you are not adequately flossing or brushing your teeth efficiently.Regardless of whether you only notice blood occasionally, please don't dismiss it because it could indicate you're getting gum disease. Allowing plaque to accumulate may result in additional serious gum illness or cavities. Read more about how to stop bleeding gums.3. Change in Gums Colour -
Everyone's gums are different in color, yet if yours has a darker or more vibrant red than usual, especially around the tooth line, it's a classic symptom of Gingivitis. The important thing is to be alert to changes - knowing your teeth and mouth more than most, therefore, remain on the lookout for any apparent changes in overall gum color or specific areas such as near the gum line.4. Gum Swelling
Healthy gums should be stiff to the touch. If you've obtained puffy or inflamed gums, this could indicate Gingivitis and indicate that you should take better treatment of your gums.Gum irritation is the body's means of notifying you of issues, in this case, indicating that bacteria from plaque have irritated your gums.Plaque adheres to the teeth and gums, forming a sticky film. If it is permitted to accumulate at the junction of the gums and tooth line, your gums will puff out in response to the irritation. Know more about the symptoms of Swollen gums.5. Gum Receding
Your gums are separating from your teeth. If your teeth appear larger than usual, you observe gum recession or gums that tear away from the roots of your teeth. It is a common indicator of the beginning of periodontal disease or tooth decay. It's not merely a normal component of the aging process.Also Read: Tooth decay & sugar: The connectionWhat are the Causes of Gingivitis?
The collection of bacterial plaque in and around the teeth is a particularly prevalent cause of Gingivitis. Plaque from teeth constitutes a biofilm that naturally forms on the teeth. It happens when germs attach themselves to the smooth exterior of a tooth.- Hormone fluctuations: These can occur during puberty, menopause, the period, and pregnancy. Gums might get more sensitive, increasing the likelihood of irritation.
- Diseases: Some disorders, like cancer, diabetes, and HIV, have been linked to an increased incidence of Gingivitis.
- Age: Gingivitis danger rises with age.
- Drugs: Medications that limit saliva production can affect a person's dental health. Dilantin, an epileptic treatment, and angina medications can produce aberrant gum tissue growth, raising the chances of inflammation.
- Family history: Those whose grandparents or parents suffered from Gingivitis are more likely to get it themselves.
- Vitamin deficiencies: Vitamin C deficiency (scurvy) and vitamin D and B12 deficiency symptoms are strongly linked to Gingivitis.
- Smoking: People who smoke regularly are more likely than nonsmokers to acquire Gingivitis.
How is Gingivitis treated?
To treat Gingivitis, you must maintain proper oral hygiene. You should also reduce your habit of smoking when you smoke and control your blood sugar level if you have it.1. Cleaning teeth -
Gingivitis early stage symptoms can be treated with cleaning teeth. Cleaning teeth reduce gum inflammation; they all eliminate plaque and tartar:- Scaling: Tartar is removed from in between and above the line of gums via scaling.
- Planing the roots: This smoothes rough regions on the root surface and eliminates plaque and tartar.
- Lasers: This procedure may be less painful and inflammatory than root planing and scaling.
2. Medications -
Gum disease can be treated with a variety of drugs, including:- To disinfect your mouth, use antiseptic mouthwash containing chlorhexidine.
- After root planing, timed-release antiseptic chips with chlorhexidine can be put into pockets.
- Antibiotic microspheres made from minocycline can be inserted into pockets after scaling and planing.
- Oral antibiotics can treat areas of gum swelling that persist.
- An antibiotic called doxycycline can help prevent radicals from triggering tooth damage.
3. Surgery -
- Flap surgery is performed. Flap surgery involves lifting the gums backward while tartar and plaque are extracted from deeper areas. The gums are then tied in place, snugly fitting around the tooth.
- Grafts of bone and tissue. Grafting may be utilized when your jaw and teeth are too injured to repair.
- Crown lengthening of the teeth. Gingivitis can cause extra gum tissue in some persons. If this is the case, a periodontist can restructure the gum and bone tissues to reveal more of the enamel.
Conclusion -
Gingivitis is a form of gum disease that is quite frequent. It is caused by bacterial accumulation on the teeth. This deposit irritates the tissues of the gums around it, causing it to become inflamed, discolored, and unpleasant to the touch.The majority of people can manage Gingivitis by practicing good oral hygiene on a regular basis. Regular dental exams can aid in the early detection and treatment of gum disease.Also read: Ayurveda Home Remedies For Bleeding Gums
Reviewed by