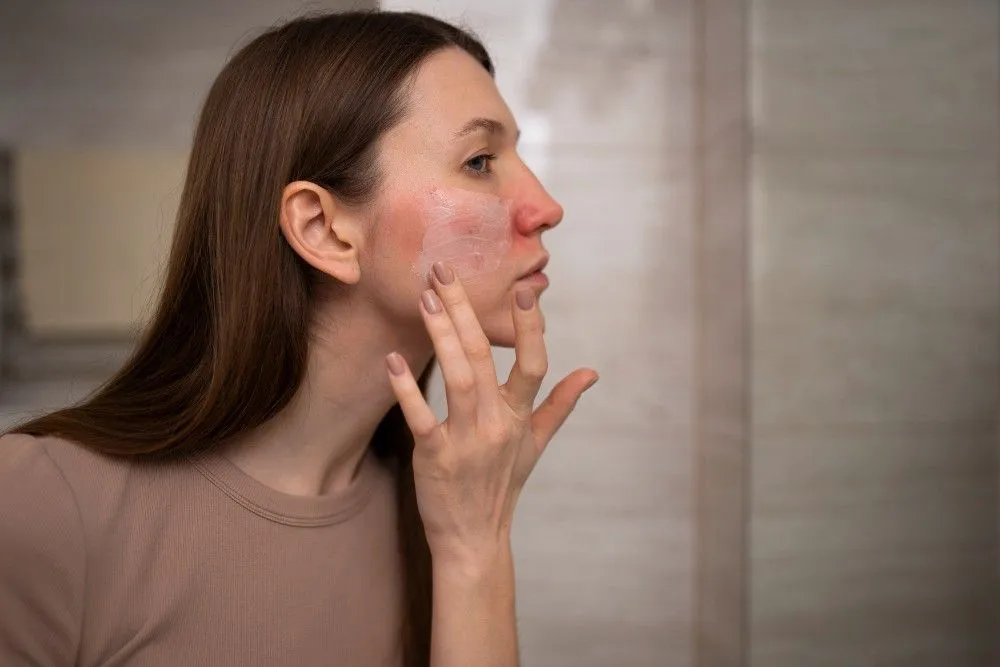
Human skin is a remarkable organ, serving as our primary barrier against environmental hazards. However, when the skin is compromised, such as through cuts or abrasions, germs can enter and cause infections. This article explores what an infected cut looks like and delves into basic care, treatment, and prevention methods.
We'll examine how the body's immune system responds to cuts, the risk of contamination, and the importance of proper healing. Read on to discover what does an infected cut look like and adopting preventive measures to ensure effective wound management and protect our overall health.
What does an infected cut look like?
In most cases, a wound with infection worsens rather than improves. Any pain, redness, or inflammation will usually worsen. The redness surrounding the cut is larger than a person's thumb, which could signal infection. Infections of the wound might also cause additional symptoms such as:- Warm the skin surrounding the cut.
- The injury produced a yellow or green discharge.
- The wound emitted a foul odor and red lines on the flesh around the area of injury.
- A fever, chills, and aches and pains are all symptoms of a bacterial infection.
- The feeling of nausea and vomiting are symptoms of nausea.
What is the Basic Care for the cuts?
The wound generally is not the reason for caution except if it is severe or extensive. However, handling a wound can enormously impact how quickly it heals. Begin by cleansing both hands and then cleaning the cut. To eliminate debris or filth, use chilled or lukewarm water instead of warm or hot water, then carefully use mild soap on the area. Apply stress to the wound until it ceases bleeding. If you are unable to prevent the bleeding, you may require sutures. To maintain the wound clean as it heals, lay a sterilized dressing over it and reapply it daily. "What does a infected cut look like?" The American Academy of Dermatology does not recommend antibiotics for minor cuts. Instead, add some petroleum jelly to the wound until it recovers. Even though the cut appears tiny, there are several explanations for why you should seek medical assistance. Tetanus injections may be required for cuts caused by a dirty or rusted instrument, and cat scratches that induce bleeding may carry bacteria present on cat claws. In either case, you should consult with a healthcare professional.What is the Prevention Infected Cut?
People with a tiny contaminated wound might be capable of treating it at home. Although a person can tell if an injury has an infection, they can start by doing the following:- Make sure all of the required supplies are clean. If you use tweezers, for example, wipe them using pouring alcohol prior.
- Please wash your hands gently with warm water and soap, then rinse them and dry thoroughly.
- If there's persistent bleeding, apply compression to the cut with a clean dressing or cotton until it stops.
- Run warm water over the wound or scrape for a few moments to clean it. Cleanse the area around the skin with soapy, warm water, but do not put soap in the area of injury.
- Ensure no debris or dirt inside the wound, including grass or stones. To get rid of the debris, use tweezers or gently clean the incision using a soft, damp towel.
- Apply a small layer of antibacterial cream or mineral oil to the wound or scrape if necessary.
- Let the skin get dry before applying gauze or an adhesive bandage. Covering minor scrapes and cuts is typically unnecessary.
What are the Treatments for infected cuts?
Severe infections of wounds necessitate immediate medical care, especially if they are accompanied by additional symptoms like fever, feeling ill, or leakage and red streaks around the wound. Antibiotics can be used to treat a bacterial infection. To fully treat the condition and prevent the germs from developing resistance against the antibiotic, the person must finish the prescribed dosage of antibiotics. Certain wounds might need additional care in addition to cleansing. A healthcare professional or nurse may need stitching to close a large or deep incision. Minor cuts are frequently closed with medicinal adhesive or strips of tape alternatively. If the wound involves dead or unclean tissue, the healthcare provider can eliminate it using a process known as exfoliation. Debridement should aid recovery while avoiding an infection from propagating. People who have been bitten by an animal or have wounds from unclean or rusted things may be in danger of tetanus and should get vaccinated. Tetanus is a very dangerous infection caused by germs that enter the human body and emit toxins that harm the nerves. Tetanus can cause severe contractions of the muscles, lockjaw, and illness.What are the risk factors of being infected by a wound?
Cuts, grazes, and other skin breaks may become contaminated when germs enter and grow in the area of injury. Bacteria can enter the body through the skin, the natural environment, or the substance which triggered the injury.- Cleaning and maintaining the wound correctly is critical to limit the danger of infection.
- The likelihood of infections of wounds increases if:
- The wound is deep, big, or has a sharp edge.
- Penetrating the wound with dirt or other particles.
- The wound was caused by a bite by an animal and a human being.
- The cut was caused by an injury with a dirty, rusted, or germ-containing instrument.
What are the Complications you face if you haven't got proper treatment?
If a wound infection is not treated, the bacterial infection will spread to various areas of the body, resulting in serious problems such as:- Cellulitis is an infection that affects the skin's outermost layers and tissues that causes inflammation, redness, and soreness in the affected region. Fever, disorientation, nausea, and puking are other symptoms.
- Osteomyelitis is an infection by bacteria of the bone that causes discomfort, irritation, and swelling in the affected area. Additional signs associated with osteomyelitis include tiredness and fever.
- Sepsis is a severe immunological response that can occur when infections pass through the blood circulation. Sepsis is a life-threatening condition that can cause numerous organ failures.
- Necrotizing fasciitis occurs when infection by bacteria propagates deep beneath the layer of skin to a tissue identified as the fascial lining. Necrotizing fasciitis is a medical condition that causes significant skin harm and discomfort, and it has the potential to spread all over the body.
Conclusion -
Bacteria might enter and spread inside the wound, resulting in infection. Washing and treating cuts, grazes, and other minor wounds as soon as possible is the best approach to avoid infection. On the other hand, people with bigger, deeper, or more severe wounds should have the injury treated by an experienced healthcare practitioner. Increased inflammation, redness, and pain around the area of injury are indicators of wound infection. A mild infection caused by a tiny wound can be treatable at home by recleaning and dressing the site. On the other hand, more severe infections of wounds necessitate immediate medical care, especially if there is a fever, feeling ill, or drainage and red streaks around the site.
Reviewed by